Related Resources: fluid flow
Siphon Flow Rate Equation and Calculator
Siphon Flow Rate from Small Pipes Equation and Calculator.
The effective (differential) head, Δh, over the pipe or siphon has to be measured as accurately as possible, but the installation also has to be practical. For field measurements a transparent hose acting as a siphon, as illustrated below, will be found useful. By keeping the hose in a vertical position Δh can be read from a scale. Since siphon fluid source level will drop as soon as the device is installed, a meter may be placed and read quickly to obtain a reasonably accurate Δh-value.
From a hydraulical viewpoint, two types of pipes (or siphons) can be distinguished:
- ‘small diameter pipe’, being a pipe with a .length L considerably more than D,
- ‘large diameter pipe’, which has a relatively short length of 6 Dp ≤ L ≤ 20 Dp,.
Related:
Siphon Flow and Discharge Rates Tables and Charts
Preview: Siphon Flow Rate through Small Pipes Calculator

Determining operating head height (Δh)
Siphon Flow Rate:

For ‘small diameter pipes’ friction losses in the pipe play a significant role and the head loss coefficient is estimated to equal:
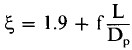
Symbols used:
Q = Discharge (m3/s)
Dp = Siphon internal diameter (m)
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2)
Δh = operating head (m) Note: That head height will change when siphoning from a fixed volume.
f = friction loss coefficient (0.019)
L = Siphon length (m)
ε = Friction losses (dimensionless)
Discharge Measurement Structures
Third Edition
M.G. Bos
International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement / ILRI
Related
- Siphon Flow and Discharge Rates
- Venturi Flow Equation and Calculator
- Mass Flow Rate Fluids Flow Equation
- Maximum Storm Drain Pipe Flow Rate Pipe Flow Rate
- Fluid Volumetric Flow Rate Equation
- Natural Gas Pipe Flow Rate Calculator
- Hazen-Williams Water Pressure Drop Flow Rates Equations and Calculator
- Babcock Steam Flow Rate Formula and Calculator